Understanding Psoriatic Arthritis: A Comprehensive Guide

Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a complex, chronic inflammatory disease that affects both the joints and the skin. Often associated with psoriasis, a condition characterized by red, scaly skin patches, PsA presents a unique set of challenges for those who live with it. This comprehensive guide delves into the many facets of psoriatic arthritis, including its symptoms, causes, diagnostic process, and a variety of treatment options. By exploring current research and patient care strategies, this article aims to provide valuable insights for individuals seeking to manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
With millions of people worldwide affected by psoriatic arthritis, understanding this autoimmune disorder is crucial. Advances in medical research and technology have led to significant improvements in diagnosis and treatment over recent years. Early intervention, personalized care, and a combination of pharmaceutical and lifestyle approaches are key to managing PsA effectively.
What Is Psoriatic Arthritis?
Psoriatic arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, leading to inflammation in the joints and skin. While it is closely linked to psoriasis, not every person with psoriasis will develop PsA. The condition typically manifests as joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, and can affect any joint in the body—from the small joints in the fingers and toes to larger joints like the knees and spine.
Unlike other forms of arthritis, psoriatic arthritis often follows an asymmetric pattern, meaning that it may impact one side of the body more than the other. This uneven distribution of symptoms can sometimes complicate the diagnostic process. Moreover, PsA may present with varying degrees of severity, ranging from mild discomfort to severe joint damage that can significantly impair mobility.
Early recognition of psoriatic arthritis symptoms is essential to prevent long-term joint damage. Patients are encouraged to seek medical advice if they experience persistent joint pain, swelling, or stiffness, particularly if accompanied by psoriasis symptoms.
Common Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
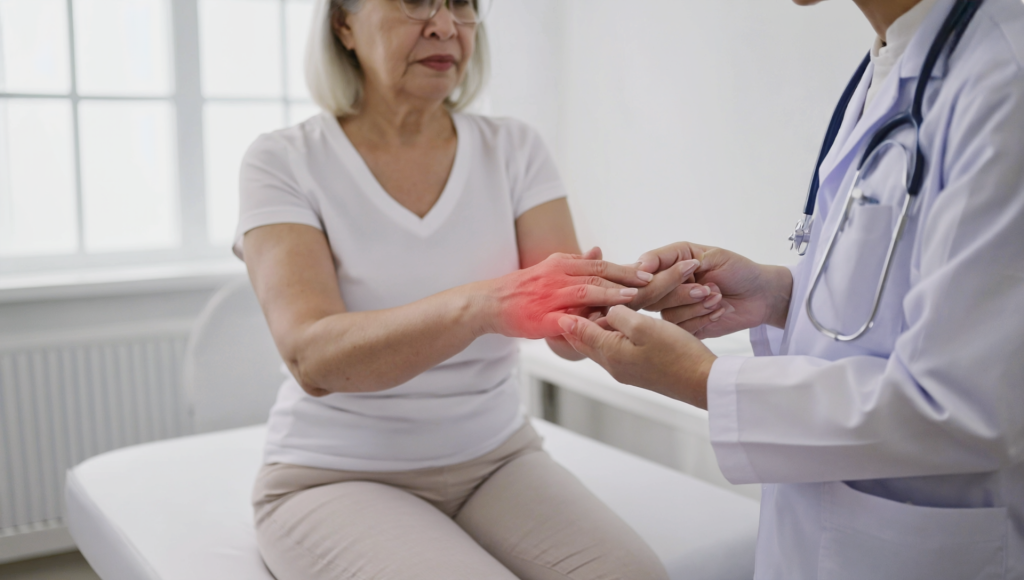
The symptoms of psoriatic arthritis can be diverse and vary greatly among individuals. Some common early warning signs include joint pain and stiffness, particularly in the mornings or after periods of inactivity. Swelling in the joints, often accompanied by redness and warmth, is also typical. Many patients report fatigue and a general sense of malaise, which can further impact daily activities.
In addition to joint-related symptoms, changes in the skin and nails are frequently observed. Psoriasis may present as red, scaly patches on the skin, while nail abnormalities such as pitting, discoloration, or separation from the nail bed can be indicators of PsA. In some cases, inflammation may also affect the eyes, leading to conditions like uveitis.
Recognizing these early symptoms can lead to prompt diagnosis and treatment, reducing the risk of irreversible joint damage. Patients experiencing these signs should consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation.
Causes and Risk Factors
The precise cause of psoriatic arthritis remains unclear, but it is believed to be the result of a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. Genetics play a significant role, as a family history of psoriasis or arthritis increases the likelihood of developing the condition. Additionally, certain genetic markers have been associated with a higher risk of PsA.
Environmental factors such as infections, physical injuries, and prolonged stress can also trigger the onset of psoriatic arthritis in individuals who are genetically predisposed. The interplay between these factors contributes to the abnormal immune response that characterizes the disease.
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures and be more vigilant about early symptoms. Research is ongoing to further clarify the underlying mechanisms of PsA and to identify more precise predictors of disease development.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Diagnosing psoriatic arthritis can be challenging due to its similarities with other forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Physicians typically rely on a combination of clinical evaluations, patient history, and diagnostic tests to establish a diagnosis. Blood tests are often used to check for inflammatory markers and to rule out other autoimmune conditions.
Imaging techniques, such as X-rays, MRI, and ultrasound, play a critical role in visualizing joint damage and inflammation. These tools help clinicians assess the extent of joint involvement and monitor disease progression over time. A comprehensive skin and nail examination is also crucial, as the presence of psoriasis can support the diagnosis of PsA.
Given the complexity of the condition, early and accurate diagnosis is paramount. A multidisciplinary approach, involving rheumatologists, dermatologists, and primary care physicians, can significantly improve patient outcomes by enabling timely intervention.
Treatment Options for Psoriatic Arthritis
Although there is currently no cure for psoriatic arthritis, a variety of treatment options are available to manage symptoms and slow disease progression. The primary goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and prevent joint damage.
Medications: The cornerstone of PsA management includes nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Biologic agents have revolutionized treatment by specifically targeting inflammatory pathways, thereby reducing joint damage and improving quality of life.
Lifestyle Modifications: Incorporating regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, and managing stress through techniques such as mindfulness and meditation can significantly alleviate symptoms. Low-impact activities like swimming, yoga, and walking help maintain joint flexibility without exacerbating pain.
Physical Therapy: Tailored physical therapy programs can help improve mobility, strengthen muscles around affected joints, and reduce stiffness. These programs are often customized to meet individual needs and can be a vital component of a comprehensive treatment plan.
In many cases, a combination of these approaches is employed to achieve the best possible outcomes. Close collaboration between patients and healthcare providers is essential to tailor treatment plans that address both the physical and emotional aspects of the disease.
Living with Psoriatic Arthritis
Managing psoriatic arthritis is a lifelong journey that extends beyond medical treatment. Patients are encouraged to adopt a holistic approach that includes regular medical check-ups, adherence to prescribed therapies, and proactive lifestyle modifications. Emotional support through counseling and patient support groups can also play a significant role in managing the psychological impact of the disease.
Many individuals find that engaging in regular physical activity not only improves joint function but also boosts overall mood and well-being. A balanced diet, rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can further support joint health. Additionally, adequate rest and stress management are critical in preventing flare-ups.
By integrating these strategies, patients can better manage their symptoms and maintain an active, fulfilling life. Education about the disease and a proactive approach to self-care are key to empowering individuals with psoriatic arthritis.
Ongoing Research and Future Outlook
The field of psoriatic arthritis is rapidly evolving, with ongoing research focused on understanding the underlying mechanisms of the disease and developing new treatment modalities. Recent advancements in biologic therapies and personalized medicine are paving the way for more effective and targeted interventions.
Researchers are exploring innovative approaches such as gene therapy, advanced imaging techniques, and novel drug delivery systems to enhance the accuracy of diagnosis and the effectiveness of treatments. The integration of digital health tools, including wearable devices and mobile applications, is also transforming the way patients monitor their symptoms and manage their condition on a day-to-day basis.
As our understanding of psoriatic arthritis deepens, the future looks promising for the development of therapies that not only manage symptoms but also address the root causes of the disease. Collaborative efforts among scientists, clinicians, and patient advocacy groups are essential in driving these innovations forward, ultimately leading to improved outcomes and a better quality of life for those affected.
While psoriatic arthritis remains a challenging condition, the rapid pace of medical advancement offers hope. Continued research and technological innovation are key to unlocking more effective, personalized treatment strategies that will benefit patients now and in the future.