Exploring the Pathways in Radiology Education
Radiology is a critical field in modern medicine, bridging the gap between diagnostic imaging and patient care. As technology continues to evolve, so too does the education required to master the art and science of radiology. This article explores the comprehensive pathways in radiology education, detailing the journey from undergraduate studies to specialized residencies and fellowships. Whether you are an aspiring radiologist or a professional seeking to expand your knowledge, understanding the educational landscape of radiology is essential for success.
The study of radiology encompasses a diverse range of topics including physics, anatomy, and the principles of imaging technology. With the rapid integration of digital advancements, radiology education has transformed significantly over the past few decades. Today, students and professionals alike benefit from state-of-the-art training facilities, virtual simulations, and a wealth of online resources that enhance traditional learning methods.
Historical Overview of Radiology Education
The field of radiology has its roots in the discovery of X-rays in the late 19th century. Initially, the use of X-rays was experimental, and education in this field was rudimentary. Early radiologists learned through hands-on experience and mentorship, often working closely with pioneers in the field. As the applications of radiology expanded, so did the need for formalized education programs.
By the mid-20th century, academic institutions began developing structured curricula for radiology. Medical schools integrated radiology courses into their programs, and dedicated residencies emerged to provide in-depth clinical training. These early programs laid the foundation for what has become a highly specialized and technologically advanced field.
Educational Pathways in Radiology
The journey to becoming a radiologist typically begins with a strong foundation in general medicine. Aspiring radiologists must first complete an undergraduate degree with a focus on the sciences, followed by medical school. During medical school, students are introduced to the basics of diagnostic imaging and the pivotal role it plays in patient care.
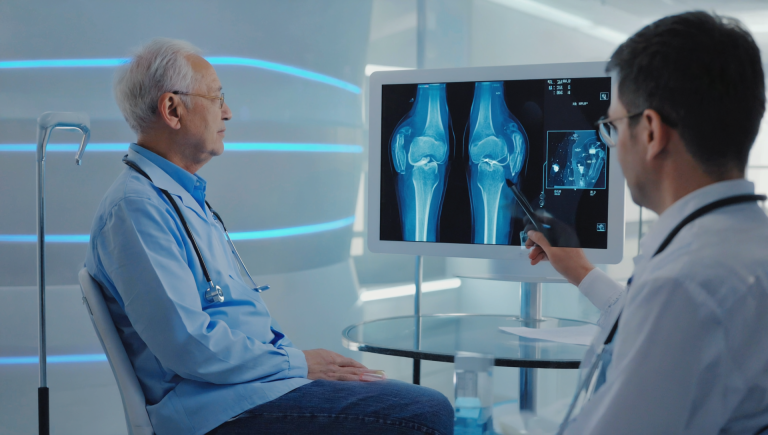
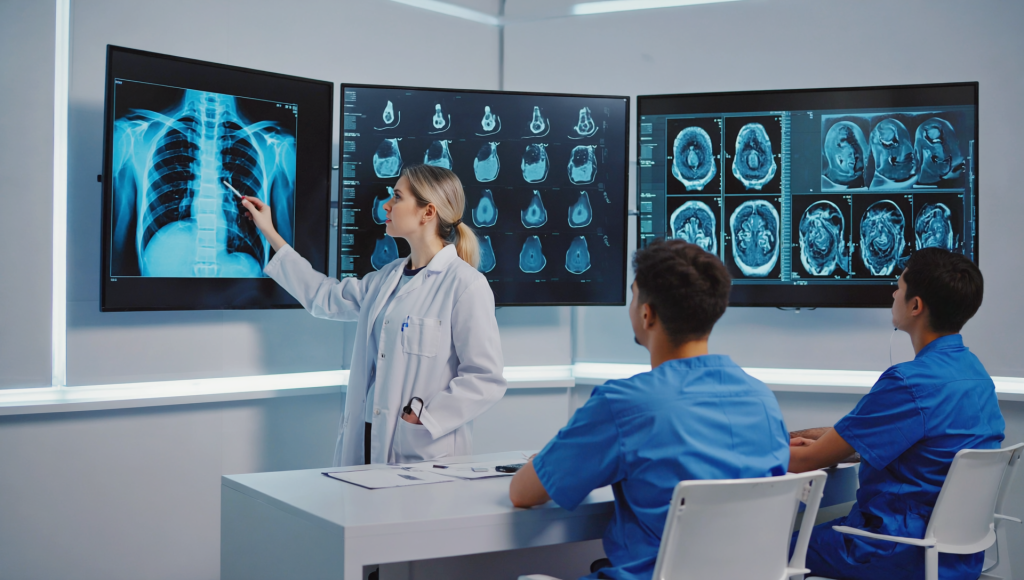
Following medical school, graduates enter residency programs in radiology. These residency programs usually last between four to five years and provide intensive training in various imaging modalities such as X-ray, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound, and nuclear medicine. Residents gain practical experience by working in hospitals and imaging centers, under the supervision of experienced radiologists.
After completing a residency, many radiologists choose to pursue fellowships to specialize further in areas such as interventional radiology, pediatric radiology, neuroradiology, or musculoskeletal imaging. Fellowships provide additional, highly specialized training and are crucial for those who wish to focus on a particular aspect of radiology. Throughout this educational journey, continuous learning is emphasized through conferences, workshops, and certifications that keep professionals updated on the latest technological advancements and clinical practices.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact on Education
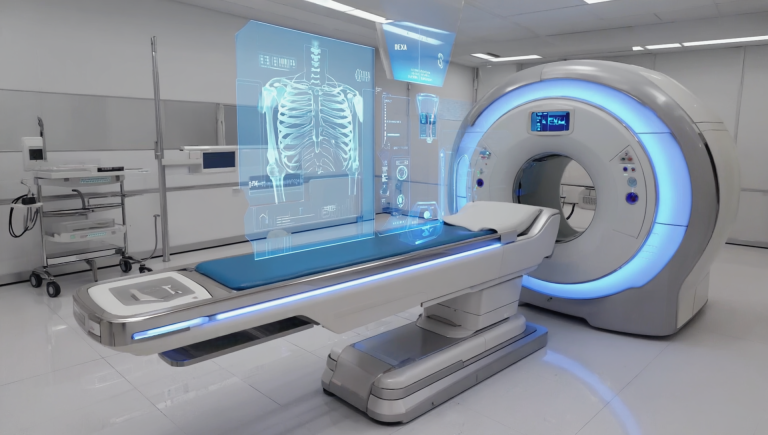
One of the most significant changes in radiology education has been the integration of cutting-edge technology into the learning process. Digital imaging, artificial intelligence, and virtual reality have transformed traditional teaching methods, allowing for a more immersive and interactive experience.
Modern radiology training now often includes virtual simulations that replicate clinical scenarios. These simulations enable students to practice diagnostic techniques in a risk-free environment, enhancing their skills before they encounter real patients. In addition, online platforms and digital libraries provide access to vast amounts of imaging data, research papers, and case studies that enrich the educational experience.
Artificial intelligence is also playing a growing role in radiology education. AI-driven tools assist in image analysis, helping students learn how to identify subtle abnormalities that may indicate early stages of disease. This technology not only improves diagnostic accuracy but also accelerates the learning curve by offering instant feedback and tailored educational content.
Career Opportunities and Professional Growth
Radiology education opens the door to a wide range of career opportunities. Beyond clinical practice, radiologists can pursue careers in research, academia, and industry. Many professionals contribute to the development of new imaging technologies or work as consultants in healthcare institutions, helping to design and implement efficient diagnostic systems.
Academic careers in radiology involve teaching the next generation of medical professionals and conducting research that advances our understanding of imaging techniques. Radiologists in research often collaborate with engineers, data scientists, and other medical specialists to push the boundaries of what is possible in diagnostic imaging.
The professional growth of a radiologist is marked by continuous learning and adaptation. Ongoing education, including participation in conferences, certification courses, and workshops, is crucial for staying current with technological and clinical advancements. This commitment to lifelong learning ensures that radiologists can provide the best possible care to their patients while also contributing to the evolution of the field.
Challenges in Radiology Education
Despite the many advancements in radiology education, challenges remain. One significant obstacle is the high cost of training and advanced technology, which can limit access for some students and institutions. Additionally, the rapid pace of technological change means that educational curricula must be constantly updated to remain relevant.
There is also the challenge of balancing theoretical knowledge with practical skills. While virtual simulations and digital resources have greatly enhanced the learning experience, nothing can fully replace the value of hands-on training in a clinical setting. Ensuring that students receive ample real-world experience is essential for developing competent radiologists.
Finally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into clinical practice presents both opportunities and challenges. Educators must find ways to incorporate these technologies into the curriculum while also addressing concerns related to data privacy, ethical considerations, and the potential for technology to change the role of the radiologist.
Future Directions in Radiology Education
Looking forward, the future of radiology education is poised to be shaped by further technological innovation and evolving clinical practices. The incorporation of more advanced virtual reality simulations, real-time data analytics, and AI-driven diagnostic tools will continue to enhance the learning process.
Educational institutions are increasingly forming partnerships with technology companies and healthcare providers to develop integrated training programs that prepare students for the realities of modern medical practice. These collaborations are essential for creating a dynamic and responsive curriculum that keeps pace with rapid advancements in imaging technology.
Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on personalized learning, where educational programs are tailored to the unique needs and learning styles of individual students. This approach not only improves educational outcomes but also ensures that future radiologists are better equipped to meet the diverse challenges of clinical practice.
As the field of radiology continues to expand, the need for specialized training and ongoing professional development will only increase. Future radiology education will likely focus on multidisciplinary collaboration, integrating insights from fields such as bioengineering, computer science, and data analytics. This holistic approach will empower radiologists to harness the full potential of emerging technologies and to drive forward innovations in diagnostic imaging.
In conclusion, the pathways in radiology education are evolving rapidly, influenced by technological advancements and a growing demand for specialized knowledge. From undergraduate studies to advanced residencies and fellowships, the journey to becoming a radiologist is both challenging and rewarding. With a commitment to continuous learning and innovation, the future of radiology education promises to be as dynamic as the field itself, offering exciting opportunities for those dedicated to mastering the art and science of medical imaging.